- TOP
- Support & Inquiries
- Technical Glossary
- Thermal resistance
Technical Glossary
Thermal resistance
[Thermal resistance]
There are various types of thermal resistance, such as heat transfer resistance, thermal resistance due to convection, thermal resistance due to radiation, and contact thermal resistance, though heat transfer resistance is often used for evaluation of a heat conductor and heat conductive tests. This is simply called thermal resistance.
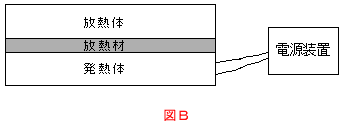
Thermal resistance is the coefficient that indicates the difficulty of heat flowing as part of the movement of heat that occurs when an object is subjected to heat. Units are indicated in K/W or ℃/W. When a heat conductor as in Thermal resistance is the coefficient that indicates the difficulty of heat flowing as part of the movement of heat that occurs when an object is subjected to heat. Units are indicated in K/W or ℃/W. When a heat conductor as in Figure B is sandwiched between a heat-generating object such as a CPU and a heat-dissipating object such as a heat sink, supplying electric power (W) to a heat-generating object, i.e., an amount of heat, means that a temperature difference will be produced at both ends of the heat conductor (the heat-generating object and heat-dissipating object) . The value where this temperature difference is divided by the electric power will be the thermal resistance.Figure B is sandwiched between a heat-generating object such as a CPU and a heat-dissipating object such as a heat sink, supplying electric power (W) to a heat-generating object, i.e., an amount of heat, means that a temperature difference will be produced at both ends of the heat conductor (the heat-generating object and heat-dissipating object) . The value where this temperature difference is divided by the electric power will be the thermal resistance.
In other words, the relationship will be
thermal resistance (℃/W) =temperature difference (℃) ÷ sign amount of heat for a heat source (W)
A smaller temperature difference at both ends of a heat conductor means that heat is more readily transferred, so the level of heat-conducting action is quite high. In other words, a substance with a small thermal resistance is preferred as a heat conductor.
Thermal resistance is not a specific value (physical property) for a substance, so values will differ even with the same material depending on the environment and conditions of usage. In other words, saying thermal resistance means a value indicating heat-conducting characteristics incorporating various conditions such as the state in which a heat-conducting material is placed, the thermal conductivity of the material, material thickness, and the material dimensions.
- Customization
- We also develop custom products to meet our customers’ individual needs. Contact us today!
